Intelligent Manufacturing of Industrial Automation Integration Industry Research and Analysis Report
2019-02-11

|Industry Overview
Industrial Automation Integration is the foundation of intelligent manufacturing and the core of realizing “Made in China 2025.”
Due to trade wars and financial policies, China’s real economy faces significant difficulties and uncertain development. Over the past five to ten years, China’s manufacturing has taken a significant step in the process of industrial automation transformation and is experiencing a period of rapid development.
Using advanced means such as robotics and the Internet to transform traditional production methods has become the development trend in China’s manufacturing industry. As a PE institution, transforming and upgrading China’s manufacturing industry is always one of our core concerns. Growing with China’s manufacturing industry has always been our value investment philosophy.
At present, JD Capital has invested in more than 70 companies in advanced manufacturing, among which more than 20 enterprises have been successfully listed, including Shenzhou High-Speed Rail, Haozhi Mechanical and Electrical, etc.
|Market Scale
The domestic robot market has been increasing in the past five years. According to IFR, China has been the world’s top industrial robot application market for several years, with cumulative annual sales of 89000 units in China in 2016, up 30% year-on-year. The cumulative sales for 2017 were about 138000 units, up 55% year-on-year. Driven by downstream demand, the sales of industrial robots in China have continued to grow rapidly. It is estimated that the industry growth rate is expected to remain above 25%.
|Industry Driven
1. The loss of demographic dividend and rising labor costs caused rising economics of achieving industrial automation to replace labor.
2. The difficulty of managing personnel increases, and industrial automation helps improve product quality stability.
3. Alternative need for security work.
4. The need for market competition.
5. Policy-driven volume.
|Investment Opportunities
We believe that the process of automation and intelligence will not be interrupted by changes in the trade and financial environment, but rather the head enterprise will take this opportunity to accelerate the transformation of industrial automation integration, thus pulling away from competitors.
Companies engaged in industrial automation integration are experiencing the best and worst times. The rapid growth of downstream demand and the increasing scale of the business is accompanied by intensifying competition, rising labor costs for engineers, increasing customer requirements, and the continuing challenge of an expanding capital gap. The number of companies listed through IPO or M&A is increasing year by year, but the high growth of some companies is accompanied by the problem of capital chain tension or even breakage.
The industrial automation integration industry will maintain high growth in the next three to five years. Related companies will share the growth dividend, and the field scale will grow rapidly. Outstanding companies are expected to receive help from the capital market and become leaders in various fields.
Part 1 Industry Analysis
The process of automation and intelligence will not be interrupted by changes in the trade and financial environment, but rather the head enterprise will take this opportunity to accelerate the transformation of industrial automation integration, thus pulling away from competitors.
The industrial automation integration industry is the foundation of intelligent manufacturing and is a way to achieve “Made in China 2025.” Intelligent manufacturing, also known as Industry 4.0, is essentially based on industrial automation, upgrading and transforming the traditional manufacturing industries through information technology such as the Internet. The industrial automation integration industry provides products that are a combination of hardware and software, integrating robots, automation equipment, control software, MES (Manufacturing Execution System), etc., with the characteristics of non-standard equipment customization.
1.1 Industry Chain Introduction
The upstream of the industrial chain of industrial automation integration include gearboxes, servo motors, control system, ontologies, software, etc. The downstream applications are extensive, covering automotive, consumer electronics, home appliances, food, and medicine, covering almost all industrial fields.
Upstream:
The materials required for industrial automation integration include industrial robots, various mechanical components, and electrical components, with robots being the most significant cost element for automation integration.
The global supply of industrial robots is mainly in the hands of the “Big Four” (Fanuc, ABB, Kuka, Anchuan), with a market share of over 50%. The mainstream customers in the industrial automation integration industry usually limit the selection of industrial robots to the “Big Four” brands, resulting in the relative strength of the “Big Four.”
Industrial robot prices are relatively transparent and correlate well with purchase volume. Though most mechanical components and electrical components are affected by factors such as supply and demand, the price will fluctuate to a certain extent. Still, overall the domestic mechanical and electrical components market is more mature, the supply of products is more stable, and the impact on automation integration enterprises is relatively small. Part of the high-technology components produced by several famous foreign enterprises. Whether such components can be sustained and stable supply to domestic intelligent manufacturing equipment enterprises has a specific impact.
Downstream:
Industrial automation integration companies serve a wide range of fields, including the manufacturing of electronics, automotive and parts, medical equipment, machinery equipment, etc. Automated production equipment is a necessary infrastructure for the production activities of downstream companies. Therefore, the demand for industrial automation integration equipment will increase as companies’ production lines renew or rebuild.
Among them, the electronics and automotive industries have become essential for industrial automation and intelligent transformation due to their large scale, a large number of workers, and high product yield requirement.
High market concentration in the electronics manufacturing, automotive and construction machinery industries, with larger head enterprises and more abundant capital, makes they are more robust relative to the industry.
The industry is still in a rapid development period. The industry concentration is low, relative to the upstream and downstream have specific bargaining power, but relative to some of the leading customers, bargaining power could be more robust. As this industry’s concentration increases and the head enterprises’ scale rises, the bargaining power will gradually improve.
1.2 Industry Policies
This industry is managed by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China is mainly responsible for formulating industry planning, policies, and standards, monitoring the daily operations, promoting the development of major technical equipment and independent innovation, guiding the promotion of information technology construction, coordinating the maintenance of national information security, etc. Meanwhile, the State Council and the Development and Reform Commission also have significant policy influence on the development of the industry.
1.3 Industry Scale
Industrial automation integration is the basis for intelligent manufacturing. Industrial automation integration requires automation transformation and upgrading according to the enterprise’s production organization model, quality management system, and specific industrial characteristics.
The Siemens plant in Amberg, Germany, is currently the most advanced digital factory in the world. It is considered the closest to the Industry 4.0 concept, in which nearly 75% of production operations have been automated.
The perfect combination of hardware and software systems of manufacturing systems through industrial automation integration has become the typical form of current intelligent manufacturing factories.
Compared with traditional industrial powerhouses, China’s manufacturing industry development is uneven. A few electronic and automobile production enterprises have a high degree of automation, while most factories still rely heavily on manual operations. Overall, there is a trend of human-intensive manufacturing, Industry 2.0 (mechanization of large-scale manufacturing), and Industry 3.0 (industrial automation) co-existing.
The foundation of industrial automation is relatively weak. In the context of rising labor costs, and domestic industrial upgrading, the automation integration of China’s manufacturing industry has been in a rapid development stage in recent years.
1.3.1 Market Scale
Industrial automation integration belongs to the non-standard equipment manufacturing industry. The customers are distributed in various fields of the national economy, and the industry scale is difficult to accurately count, so there is a lack of mature and credible market data.
During the decades of development of industrial automation, the integration of robots as the core carrier and other auxiliary equipment has become the main mode to realize industrial automation. Therefore, we use indicators such as the scale and density of industrial robots to measure the industry scale and growth rate of industrial automation integration.
Due to the uneven development of industrial automation integration in China, most of the industry is the hardware integration of robots and auxiliary equipment, and the integration of MES, PLM and other related software implementation is relatively small. From the specific industrial form, the robot is a standardized product, the industry is mature, and the overall industry scale is relatively clear. In China’s current industrial automation integration industry contracts with customers, the price of robots accounts for about one-third of the contract amount, usually no more than one-half, which can be inferred from the overall market size of the industrial automation integration industry.
Globally, industrial robot sales stabilized at around 115000 units per year between 2005 and 2008. Since 2010, the rising level of automation in industrial production and continuous innovations in industrial robotics have led to a significant acceleration in the demand for industrial robots. In 2017, industrial robot sales rose sharply to around 380000 units. From 2010 to 2017, the global production of industrial robots grew at a GAGR of 17.8%. The growth rate of industrial robot sales is expected to remain high in the next three years.
Figure 2: Global robot sales and growth rate
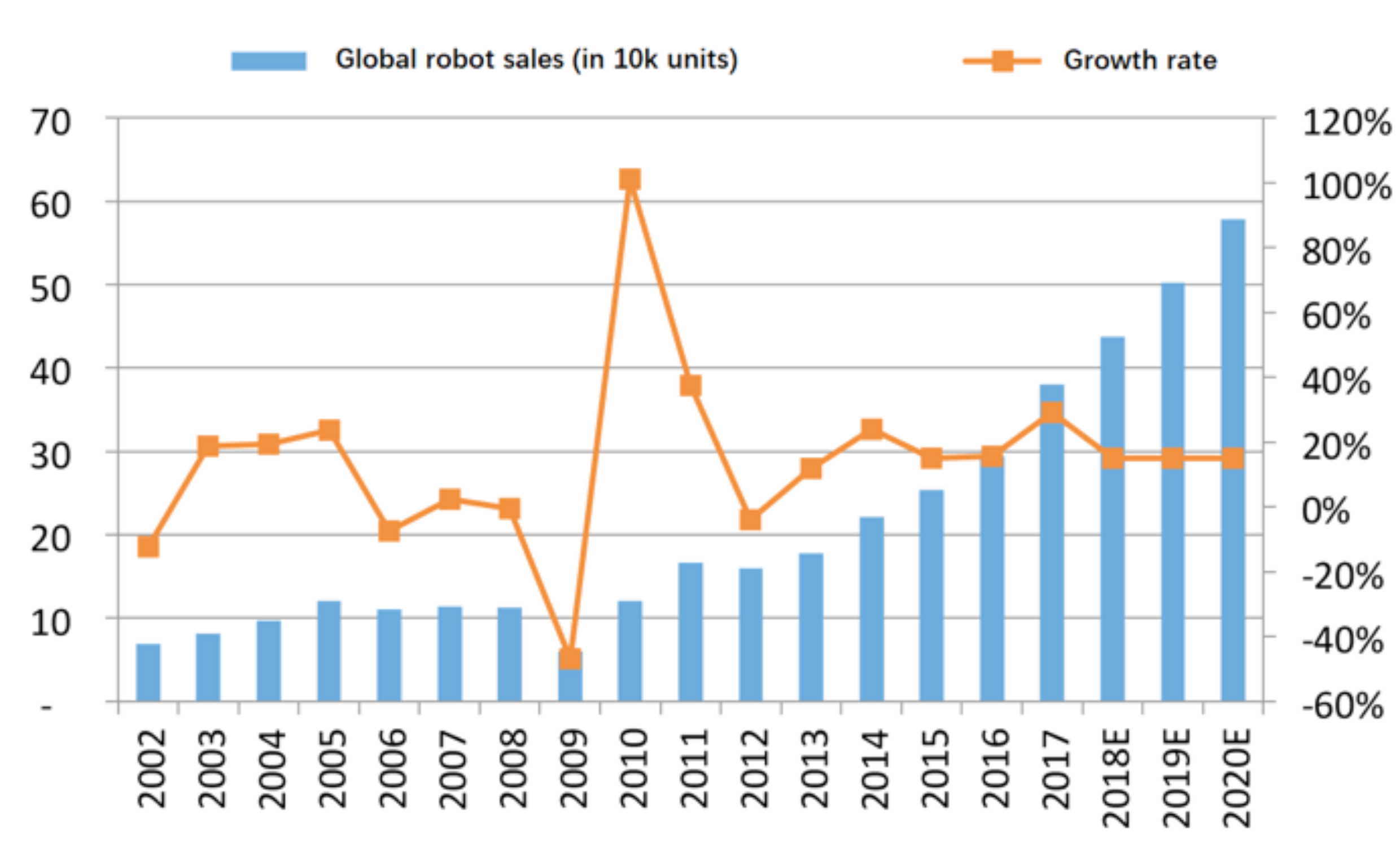
Source: IFR, JD Capital
In the past five years, the domestic robot market has grown rapidly. According to IFR statistics, China has become the world’s largest industrial robot application market for several years. Cumulative annual sales for 2016 were 89000 industrial robots in China, up 30% year-on-year. Cumulative sales for 2017 were approximately 138000 units, up 55% year-on-year. Driven by downstream demand, China’s industrial robot sales continue to grow rapidly, with a conservative estimate that the industry growth rate is expected to remain above 25%.
Figure 3: China’s industrial robot sales and growth rate
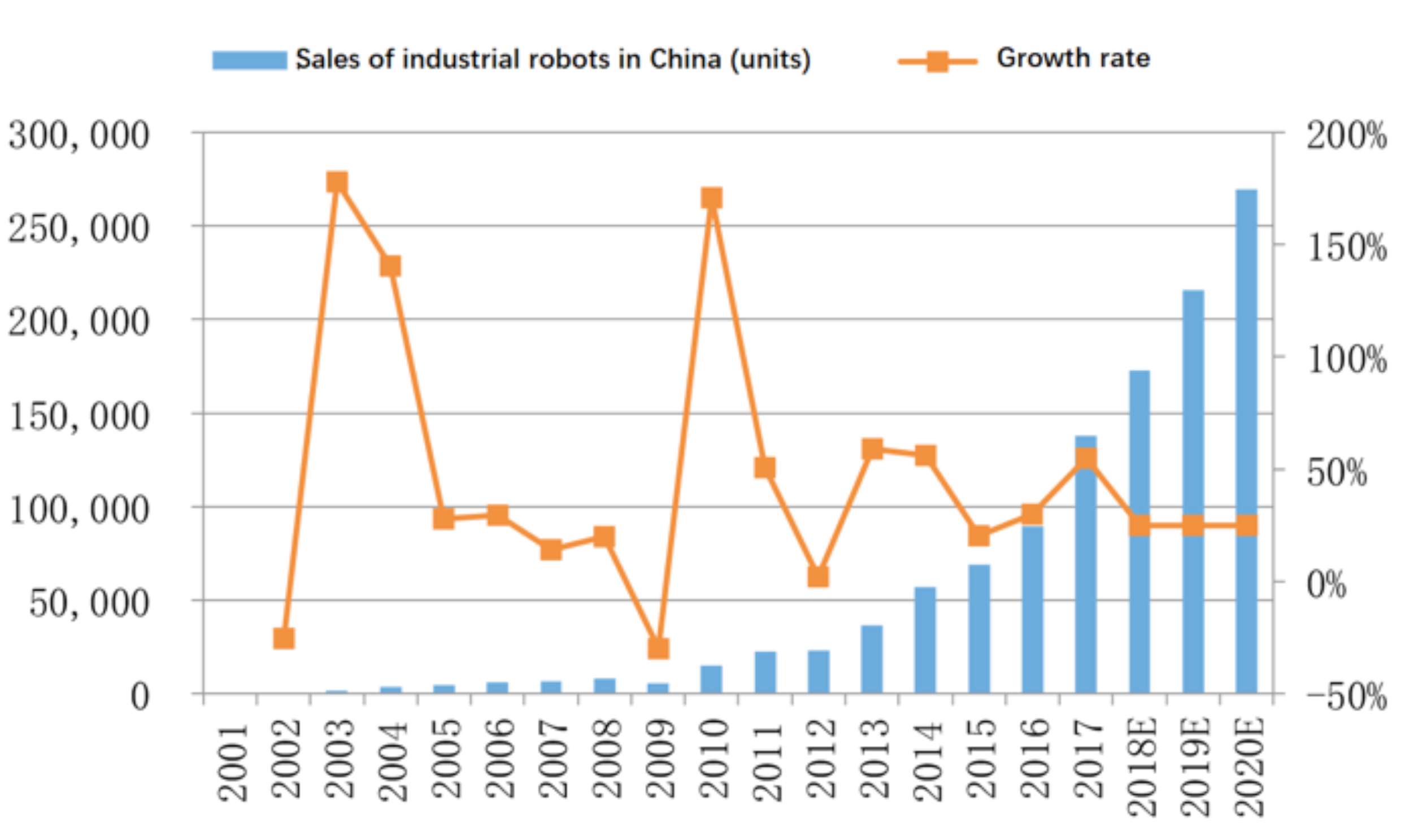
Source: IFR, MIIT, JD Capital
In 2017, China’s industrial robot sales were about 138000 units, and the price of a single robot ranges from more than 100000 to more than 500000, with a wide range of prices. The tiny robot is larger and can be conservatively projected at RMB 200000 per unit. The market size of domestic industrial robots is about RMB 27.6 billion. According to the cost ratio of industrial robots in the industrial automation integration industry, if it is a hardware-based automation production line, the robot cost ratio is 40%-50%. Including digitalization, information technology, MES, and other software integration applications, add 20% or even more software sales. Comprehensive judgment of the robot in industrial automation integration sales accounted for about one-third of the projection of China’s industrial automation integration market size of about 82.8 billion yuan.
1.3.2 Market composition and growth judgment
Taking the statistical analysis of industrial robot application areas to see the market composition integration, electrical and electronic equipment, and device manufacturing has overtaken automotive manufacturing as the primary application industry in the Chinese market, with nearly 50000 units sold in 2017, accounting for 35.2% of total sales in the Chinese market, an increase of 5.2 percentage points compared to the previous year. Automotive manufacturing remains an exceptionally essential application industry, with 43000 new robots added in 2017, increasing slightly to 31.2% of total sales in the Chinese market. In addition, the metal processing industry (including machinery and equipment manufacturing) and other manufacturing sectors have also shown growth.
According to the Robotics Industry Development Plan (2016-2020), “Realize the large-scale application of robots in key industries and reach a robot density of 150 or more.” The actual density of robots in China was about 50 teams/million people in 2015, reached 68 teams/million people in 2016, and has grown rapidly to 88 units/million people in 2017. According to China’s industrial development goals, the robot density will reach more than 150 robots per 10000 people in 2020, and robot ownership will continue to grow rapidly. Considering the robot’s life, the growth rate of new robots exceeds 25%.
Looking at the downstream applications of industrial automation integration, the penetration rate varies significantly from field to field. Consumer electronics, home appliances, and other areas are still in the rapid growth stage, and the head of the enterprise has achieved a higher degree of automation integration applications. Second and third-tier enterprises enhance their competitiveness by improving the automation application level and increasing investment in automation. Automation integration in the automotive field tends to be mature, technology and applications have been more stable, the penetration rate is high, and domestic automotive brand companies are also increasing investment in industrial automation. The automation integration of automotive parts is still in the early stage of development, with a low penetration rate and high market potential. The penetration rate of industrial automation in other fields, such as construction machinery and metal processing, is also relatively quiet. Overall, the industrial automation integration industry is still in the growth period, especially automation integration to intellectual development, which will bring sustained industry growth.
Figure 4: Industrial automation integration industry development stage
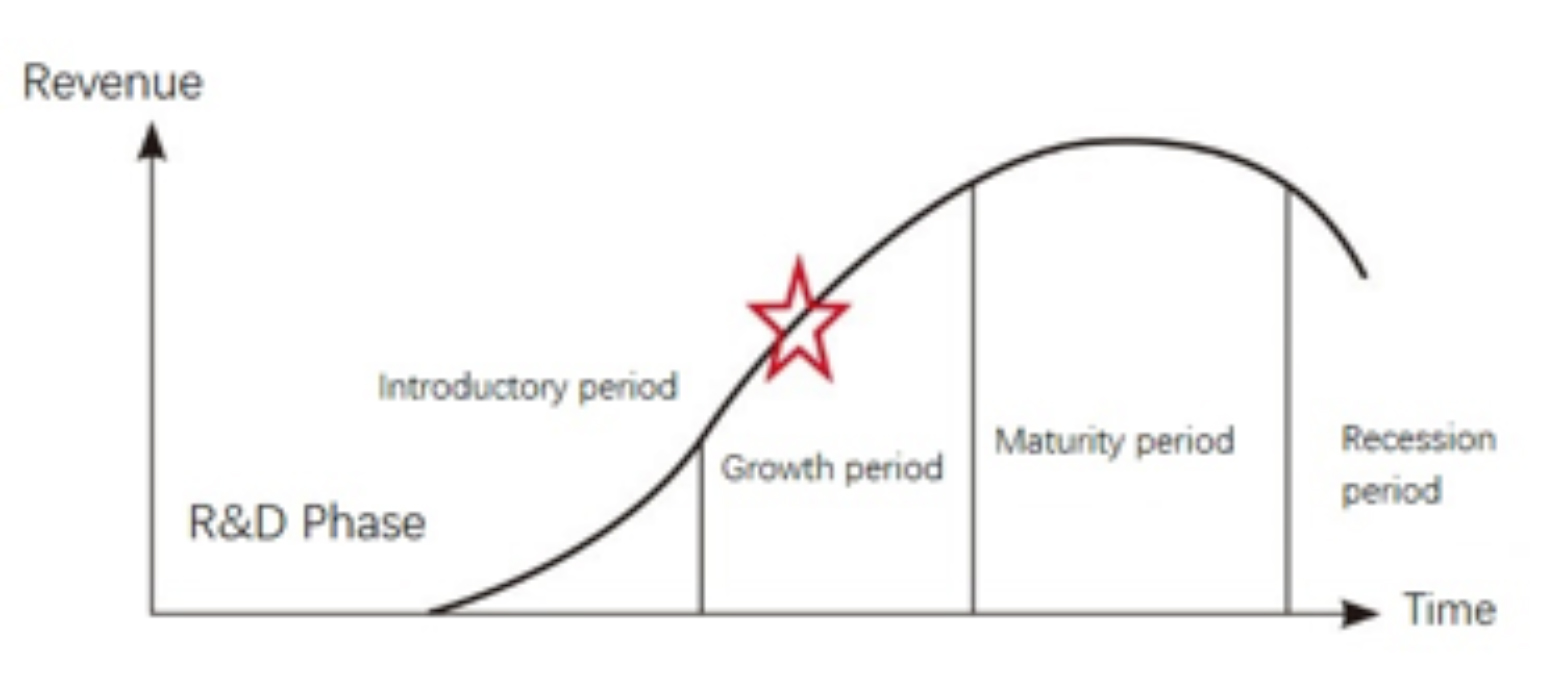
Source: JD Capital
Comprehensive view, industrial automation integration in consumer electronics, metal processing, home appliances, food, and other areas still has a significant growth space. The industry is expected to maintain a rapid growth of 25%-30% in the next three years.
1.4 Industry Drivers
1. Loss of demographic dividend, rising labour costs, rising economics of achieving industrial automation to replace labour.
On the one hand, the peak of China’s population has passed, the number of young people of working age has declined, and the supply of middle and low-end labour is insufficient. Meanwhile, the average annual wage (non-private sector) of urban employed persons in China has maintained a double-digit growth rate, increasing from RMB 37147 in 2010 to RMB 74318 in 2017, with a significant rise in labour costs. On the other hand, the price of industrial robots is decreasing, the cost of industrial automation is falling, the technology is becoming increasingly mature, and the economy of replacing manual labour is increasing.
2. The difficulty of managing personnel increases, and industrial automation helps improve product quality stability.
Younger industrial workers have more demands on themselves than the post-60s/the 70s and are unwilling to work in jobs with low wages, monotony and repetition, and poor environments. As a result, in recent years, there has been a “labour shortage” in coastal cities and a shift of some manufacturing industries to inland or Southeast Asia, where labour resources are more abundant. The demand for industrial automation tends to be strong as personnel management becomes more complex and production quality stability is difficult to guarantee.
3. Alternative needs for security work
Some jobs, such as welding, machining, heavy lifting, and civil explosives, are high-risk. Product safety is easily affected by workers’ technical proficiency, safety awareness and other aspects that are difficult to manage and prone to safety accidents. In a major safety accident, the enterprise will face huge compensation and pressure from public opinion, affecting regular operation. The enterprise’s legal person and management will have to bear the corresponding management responsibility while switching to robots can significantly reduce the risk of production safety accidents.
4. The need for market competition
China’s manufacturing industry is still in manual and semi-automatic production. Industrial automation integration can improve the manufacturing accuracy and speed of the product, thus improving product qualification rate and production efficiency.
5. Policy driven
China is currently the world’s most significant industrial manufacturing output value. However, high-end manufacturing is still mainly dominated by Japan, Europe, the US, and other countries. Low-end areas affected by competition from Southeast Asian countries are also moving out. China's manufacturing industry is significant but need to be stronger, and economic growth into an L-shaped state, the urgent need for transformation and upgrading of enterprises. To change the status quo of the manufacturing industry and follow the international trend of Industry 4.0 development, China has formulated "Made in China 2025", and the future development plan related to sectors and set up special funds to support the promotion of intelligent manufacturing projects.
Part 2 Competition Analysis
Capital and talent are the core competitive factors in the industry. The industry concentration is low, and competition is still fierce while growing rapidly. As the industry matures and the competition pattern becomes stable, the industry concentration will gradually increase. Excellent enterprises in the industry will become the leader in the niche area through IPO or M&A listing.
Competitive factors
1.Talent
The industrial automation integration industry is asset-light and intellectually intensive, requiring employees to understand downstream customers’ production processes, etc. Meanwhile, employees should have specific industry experience and knowledge of mechanical, electronic, control, computer, and sensors, to provide complete automation integration solutions. In the current market, talented practitioners can tap into customer needs and provide the optimal solution. Therefore, talents with rich experience are the industry’s most scarce resources and core elements of business development.
2.Funding
The industrial automation integration industry is relatively weak to large upstream and downstream enterprises, and bargaining power is not strong. The upstream accounts payable period is short, while the downstream is by the project progress payment. Enterprises to purchase equipment for customers often need to advance funds and high requirements for enterprise capital turnover capacity. Companies with ample capital can win many orders and expand their market share.
3.Brand
Industrial automation integration industry downstream distribution in various manufacturing industry segments, industry span, the program contains some non-standard facilities, the details of the greater variability. Automation solutions directly impact the efficiency and profitability of our customers’ systems. Therefore, customers will be more cautious when choosing industrial automation solutions. They will pay attention to whether the solution provider has a mature operation of the relevant cases and, after the completion of the solution, a large period of strict testing and inspection. Therefore, downstream customers often prefer to choose companies with successful cases in related fields for program design and implementation. Thus, industrial automation integration companies with industry brands are more likely to open the relevant market.
4.Service
As the automation integration solutions are designed according to the downstream customers’ specific production process and site, the solutions are not standardized. There may be certain problems in use after implementation, which requires a certain amount of time for testing and inspection. Then the solution provider must follow up and provide related after-sales service. Meanwhile, when customers need to build a new automated manufacturing line or replace the original line-related equipment in the future, they will also first consider the supplier who has provided them with a solution design. A solution provider with good pre-sales design and after-sales service can bind the customer quickly.
5.Technology
Industrial automation solutions integrate technologies and knowledge from mechanical, electronic, computer and communication disciplines to make each subsystem of the manufacturing system, such as production planning, operation scheduling, manufacturing processing and quality assurance, intelligent, thus forming a manufacturing system with sensing, decision-making and execution functions. In the narrow sense, industrial automation refers to manufacturing equipment with perception, analysis, reasoning, decision-making and control functions involving industrial robots, 3D printing, intelligent control systems and other frontier fields. In a broad sense, industrial automation refers to the ability to achieve the automation of the production process, intelligent, sophisticated and green equipment products. It is the integration and deep integration of advanced manufacturing technology and intelligent technology in equipment products. Therefore, this industry has formed a certain technical barrier for new entrants.
Competitive dynamics
The main competition in the industrial automation integration industry lies in the talent, capital and technical strength. Currently, the main business of listed companies is industrial automation integration or more involved in such business, the market is growing rapidly, but competition also tends to be intense. The overall industry concentration is still low. The “Big Four” need downstream industrial automation integration of their strengths in industrial robots. Still, they aim mainly to promote their robotics products and grasp high-end customers. The total market size is about 13%, and large-scale foreign companies such as Duer, Eisenman, Aifudi and other large automation companies have almost one billion sales in China. Domestic enterprises are generally small. A few domestic large-scale automation integration companies, such as Demecor (HUachangda) and Xin Song, accounted for less than 4%, unlisted small and medium-sized enterprises are still many, generally not significant.
Part 3 Future outlook
With the need for industrial upgrading in China, rising labour costs, and vigorous policy guidance and promotion, downstream demand has exploded rapidly, and the industrial automation integration industry has gained rapid development. Customers have different professional points of automation integration needs, and the technical barriers of different professional points are substantial, so the head enterprises have a strong customer synergy effect. Meanwhile, the larger business scale of the head enterprises will enhance their bargaining power over upstream suppliers and downstream customers and improve their attractiveness to capital and talent. The head enterprises’ brand and successful cases will further improve their industry influence, invest in R&D and guide the industry to further development towards intelligence and become the potential leader of big industrial data and intelligent manufacturing.
The industrial automation integration industry is facing certain risks along with high growth. Suppose there are significant economic fluctuations and deterioration of the economic environment. In that case, the willingness of downstream customers to invest in fixed assets will decline, resulting in slow growth in industry demand, further intensifying competition among companies in the industry and affecting their profitability. The industrial automation integration industry has strong non-standard customization characteristics of its products, and personnel management, project management and cash flow management are more difficult. If mismanaged, the business will be at risk.
